So with the job of White House Office of Science and Technology Policy director having gone to Dr. Arati Prabhakar back in October, rather than Dr. Alondra Nelson, and the release of the “Blueprint for an AI Bill of Rights” (henceforth “BfaAIBoR” or “blueprint”) a few weeks after that, I am both very interested also pretty worried to see what direction research into “artificial intelligence” is actually going to take from here.
To be clear, my fundamental problem with the “Blueprint for an AI bill of rights” is that while it pays pretty fine lip-service to the ideas of community-led oversight, transparency, and abolition of and abstaining from developing certain tools, it begins with, and repeats throughout, the idea that sometimes law enforcement, the military, and the intelligence community might need to just… ignore these principles. Additionally, Dr. Prabhakar was director of DARPA for roughly five years, between 2012 and 2015, and considering what I know for a fact got funded within that window? Yeah.
To put a finer point on it, 14 out of 16 uses of the phrase “law enforcement” and 10 out of 11 uses of “national security” in this blueprint are in direct reference to why those entities’ or concept structures’ needs might have to supersede the recommendations of the BfaAIBoR itself. The blueprint also doesn’t mention the depredations of extant military “AI” at all. Instead, it points to the idea that the Department Of Defense (DoD) “has adopted [AI] Ethical Principles, and tenets for Responsible Artificial Intelligence specifically tailored to its [national security and defense] activities.” And so with all of that being the case, there are several current “AI” projects in the pipe which a blueprint like this wouldn’t cover, even if it ever became policy, and frankly that just fundamentally undercuts Much of the real good a project like this could do.
For instance, at present, the DoD’s ethical frames are entirely about transparency, explainability, and some lipservice around equitability and “deliberate steps to minimize unintended bias in Al …” To understand a bit more of what I mean by this, here’s the DoD’s “Responsible Artificial Intelligence Strategy…” pdf (which is not natively searchable and I had to OCR myself, so heads-up); and here’s the Office of National Intelligence’s “ethical principles” for building AI. Note that not once do they consider the moral status of the biases and values they have intentionally baked into their systems.
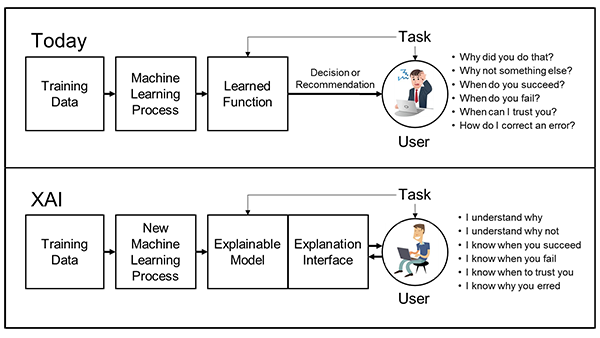
An “Explainable AI” diagram from DARPA






